What is Lean
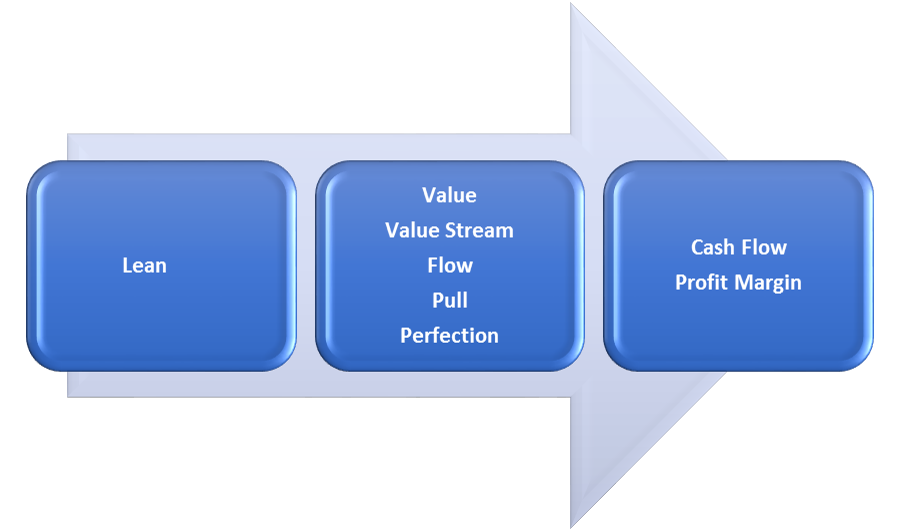
This article describes the concepts of Lean and its five principles. The key focus of Lean is to enhance value creation and waste reduction. If rightly implemented, Lean has the full potential to boost cash flow and profit margin of any business.
History of Lean manufacturing can be traced back to a thousand year. Arsenal in Venice, established in 1104 to build war ships for the Venetian Navy, is an example of continuous flow production. Some of the major breakthroughs are recorded in the history while many others might have been lost forever.
What is Lean?
Lean is creating more value for customers with fewer resources. Ultimate goal is to provide perfect value to customer, through a perfect value creation process, that has zero waste. Therefore, lean manufacturing is a culture of relentlessly work on eliminating waste, activity that does not add value from the customer’s perspective, from the manufacturing processes.
What are the Five Lean Principles?
- Value – Activities that a customer is willing to pay for
- Value stream – All steps to crate the value i.e. supplier-input-process-output-customer
- Flow – Make sure activities move through steadily and predictably
- Pull – Produce based on customer needs and specifications
- Perfection – Repeat the above steps until perfection is reached
What is Waste?
The major focus of Lean is the waste elimination. There are eight types of waste in Lean.
- Transport – Movement of people, products and information
- Inventory – Unused products, parts or information
- Motion – Movement of people creating value
- Waiting – Hold-up for parts, information, instructions, equipment
- Over production – Making more than customer need
- Over processing – Spending longer time in a process than necessary
- Defect – Produce product below requirement
- Skill – Underutilizing people skill
How to identify Waste?
One of the most useful ways to identify waste is the Value Stream Mapping, also known as Material and Information Flow Mapping. It includes all value creation processes with relevant information, such as, process time.
Tea brewing example used in the video has total process time of 3 minutes 50 seconds.
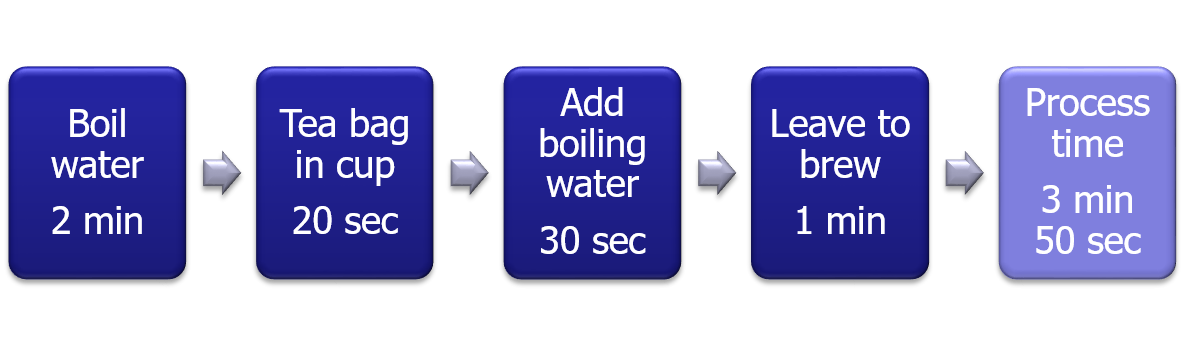
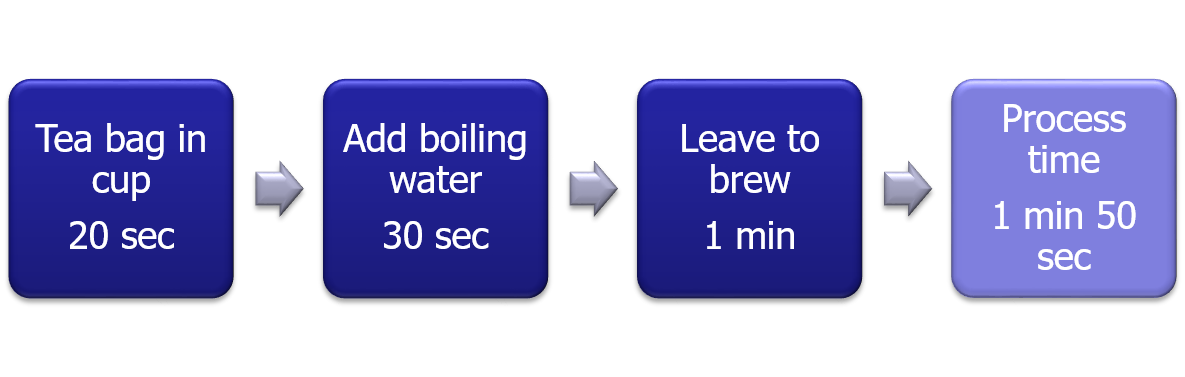
Looking at this VSM, can we identify a way to reduce process time? If optimum brewing time was 30 seconds instead of 1 minute (last process), what type of waste are we generating?
In a continuous production scenario, using pre-boiled water every time we can eliminate the first step and thereby reduce 2 minutes. In addition, it is important to identify the optimum time for each process. If brewing takes only 30 seconds, spending a full minute is an example of the waste called over-processing.
What is Flow?
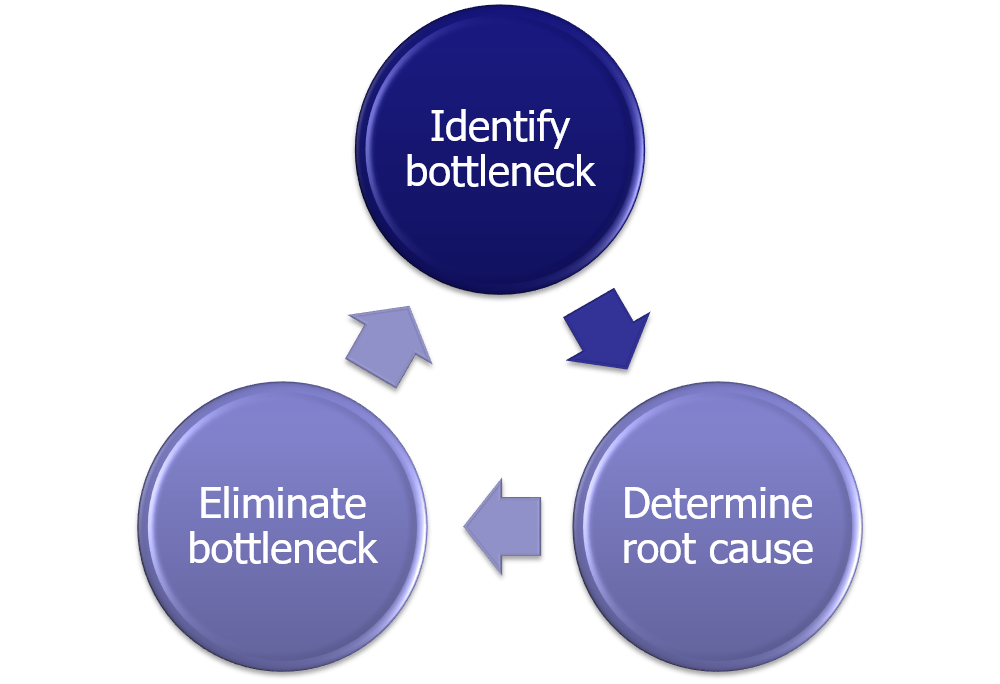
Flow is how processes move through in a value creation effort. It is important to make sure process flow is steady and predictable. This helps process planning and eliminating waste i.e. waiting. Simple problem solving techniques can be used to remove bottleneck from a process flow. For example, it starts with identifying bottleneck, then determining the root cause and finally eliminating the bottleneck.
What is Pull?
In systems where products or services are pulled through the value creation process by consumer’s demand.
Benefits of a pull system are:
- Resources are used to produce products that will immediately be sold and return a profit
- Small batch, faster identification of quality issues
- Less defective products will require disposal
Where to start?
It may take an overwhelming amount of effort to change culture and fully implement Lean. The best way to start with small good changes or improvements, also known as Kaizen. Go to your work area, identify a problem that needs to be solved, talk to the operators, determine solution and implement it. This video shows how Kaizen is implemented in Japan.
See how easy it is to solve problems when working together and taking small steps towards major improvement. It is always beneficial to include operators in the problem solving process. This not only enhances the root cause finding process but also establishes the commitment of the operators to implement and sustain the gain.